Follow a Diabetic Lifestyle: Everything Patients Need to Know
Understanding Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition when the body cannot properly regulate blood sugar (glucose) levels. This can happen due to either insufficient insulin production or the body’s cells becoming resistant to insulin. Insulin is a hormone the pancreas produces that helps cells absorb glucose for energy.

There are three main types of diabetes:
In type 1 diabetes the immune system destroys these insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas. This makes them produce (almost) no insulin at all, and in turn, leaves the person dependent on lifelong insulin. The first signs of type 1 diabetes are often parents noticed in their children or adolescents, but this disease can also develop at any age. Symptoms can be increased thirst, frequent urination, and unexpected weight loss.
Type 2 (in cases more common, typically in adults but has been increasingly diagnosed in children due to obesity). In this sort of diabetes, the body doesn’t react by siphoning out enough insulin in response to high Glucose levels. This is called Insulin resistance. Eventually, the pancreas can wear down and stop being able to make enough insulin.
Gestational diabetes is another form of diabetes that develops during pregnancy, which usually disappears following parturition (birth) but can raise the risk of Type 2 later in life. It happens when hormones that help the body control blood sugar are not working as well. It is essential to detect and manage these conditions throughout pregnancy for the health of both the mother and unborn baby.

Poor diabetes management can also trigger more serious complications like heart attacks, nerve damage, and kidney disease. So, for patients to maintain their blood sugar levels in the proper way they should be aware of diabetes and its types.
The Importance of a Healthy Diet
A healthy diet is a cornerstone of blood sugar control and more broadly, managing diabetes. Diabetic patients need high-quality nutrients with minimal effects on blood sugar levels. This includes high-quality whole foods like vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains that offer plenty of nutrients along with fiber to help stabilize blood sugar.
Diets for people with diabetes require portion control regardless of the food in question. Portion size regulation can help with the prevention of over-eating, an important factor for weight control and staving off insulin resistance. As mentioned-and for this advice to work, you must understand the glycemic index (GI). Most low Glycemic Index foods will result in a slower rise in blood sugar and provide more consistent energy all through the day. Choose low-GI whole grains, legumes, and non-starchy veggies that are often NoGut-Low, make these staples of every meal.

It is also important to exclude processed sugary and unhealthy fats. These can cause quick increases in blood sugar as well as a range of diabetic health issues. This being so, it is important to read all food labels and beware of the added sugars found in everyday items. Meal planning strategies can also help lead individuals to conscious decisions in terms of what they put into their mouths. Taking the time to plan your meals can help you find fewer choices for high-sugar food and make managing diabetes easier.
Embodying these guidelines in your daily nutrition can help stabilize blood sugar while fitting into a balanced and sustainable approach. People with diabetes must remember that they are what they eat — focusing on a healthy, balanced diet can have an important impact in controlling their disease and avoiding potential health complications.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Actually, exercise is an important way to manage diabetes. Exercise plays an important role in controlling blood sugar and promoting overall health. Engaging in regular exercise can increase insulin sensitivity, so blood sugar is better utilized. Exercise also improves health in other ways. This not only helps control blood sugar levels but also is important in managing weight, something that can become a problem for people with diabetes. In addition, exercise can help prevent heart disease and high blood pressure, two illnesses that are often found among diabetic people.

People with diabetes can do all sorts of exercise. Aerobic exercises; such as walking, swimming, and riding bikes have special benefits for the heart, while endurance required in these activities is an aid to diabetes control. They should last at least 150 minutes per week, broken into several sessions spread over several days, to provide maximal health benefits
Strength building is important for an overall exercise program. This may include lifting weights or even using one’s own body weight as resistance, and it is recommended that one does strength training (also known as “resistance training”) for at least two days a week. This type of exercise helps to build muscle mass, which is in turn conducive for glucose metabolism to occur more efficiently. It also helps to keep a person’s weight down, promoting effective diabetes management
Flexibility exercises like yoga and stretching can help increase overall mobility, and they give the benefits of muscle relaxation. In addition, exercises in this category have mental health advantages as well. And these are important because living with diabetes is often enough to stress anyone out.

It may be beneficial to add a variety of these exercises into an exercise program. Then a balanced approach can be taken, and each type of exercise will have its own benefits When one is trying to establish a good program for exercise, it is important to consider people’s varying abilities as well as what they most enjoy doing. Setting reasonable goals and slowly but steadily increasing both the intensity and duration of workouts can encourage longer-lasting compliance with an exercise program (and therefore more effective results). It is advisable to test one’s blood sugar levels before and after exercising, to make sure that one does so safely.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
One of the most important things an individual can do to effectively manage diabetes is monitoring their blood sugar. Knowing how to check blood sugar helps patients better manage their health and lower the odds of complications while living a healthier life. There are several methods for measuring blood sugar, all with strengths and weaknesses.
One of the most common ways to test blood glucose is by pricking your finger and putting a drop on a strip. The traditional approach requires pricking the finger to draw blood, which is placed onto a test strip that is fed into a glucose meter using something known as a lancing device. This process usually renders a reading in seconds, providing instantaneous results on sugar level readings. They are advised to assess their blood sugar multiple times a day for them to learn how different foods, activities, and medication impact their levels.
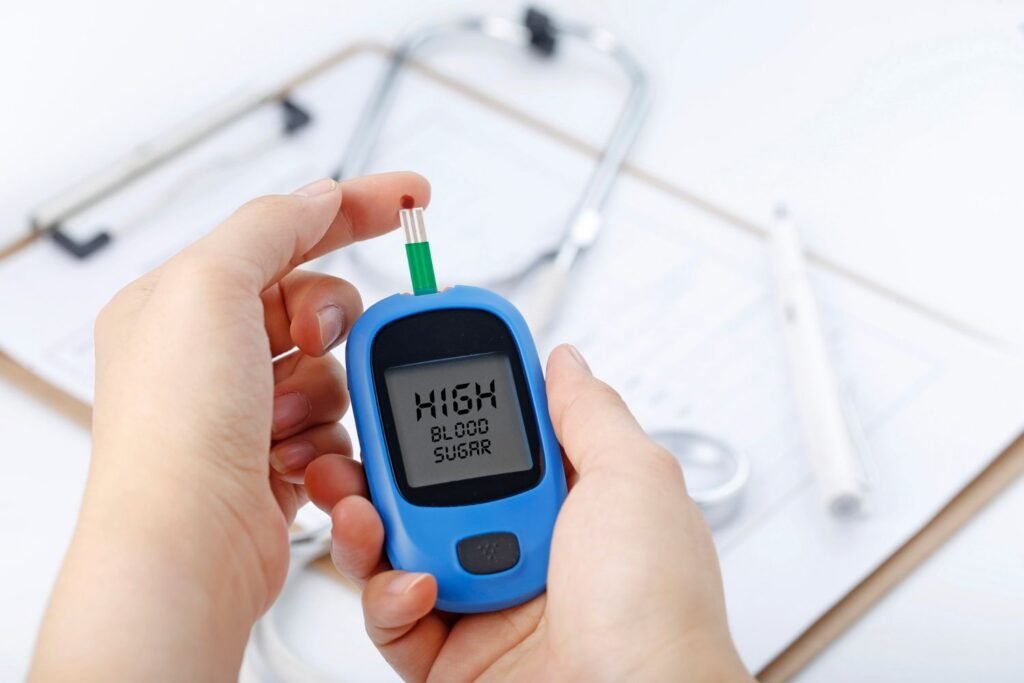
Lately, Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGM) are gaining popularity among diabetics. CGM is a small sensor inserted under the skin that tracks and monitors glucose levels around the clock. This works for a longer overall picture of glucose trends and knowing before hypoglycemia sets in so you can do something about it. A CGM can allow patients to see how their different meal choices, exercise, and even medication adherence affect their blood sugar control.
For proper diabetes management, it is critical for diabetics to understand their blood sugar numbers. Patients need to understand target ranges for fasting blood glucose, post-meal levels, and the GMI profile. If you keep a systematic log of readings that can be shown to healthcare providers, they have more solid ground for understanding your condition and creating the most appropriate treatment plan. It also allows patients to track blood sugar fluctuations and understand better how their body responds, enabling them to make certain lifestyle choices accordingly.
Managing Stress and Mental Health
It is not only the physical aspect of Diabetes that needs to be managed but there is certainly a mental health element too. Studies show that there is a relationship between diabetes with psychological problems like stress, anxiety, and depression. These conditions can worsen a person’s diabetes and make it harder to control their blood sugar. This could, for instance, result in increased stress levels and thus poorer dietary decisions as well as less compliance with medication regimens — all of which may tip the balance towards more erratic blood sugar values.
It is extremely important to understand this complex connection. Stress releases hormones (notably cortisol) that can increase your blood glucose levels. Meanwhile, fluctuating blood sugar levels can honestly make these feelings of anxiety and depression worse which in turn sets us up to be stuck in this cycle that is nearly impossible to break. Consequently, mental health management is as important an aspect of diabetes care as the rest.

There are several strategies to help overcome these challenges. Examples of mindfulness-based practices include meditation, breathing exercises, and yoga. Rather, these approaches shift the focus of individuals from future anxieties related to their diabetes care and toward present-day mindfulness. Counseling may also help people to find ways of managing their emotions and developing positive Cognitive filters.
You could also consider joining a diabetes support group. They provide a way to share experiences and encourage community. Now, these acts of brewing tea together may potentially alleviate feelings of isolation and greatly benefit one’s psychological state as a whole.
These mental health tools are a key component of the diabetic lifestyle that is necessary to succeed at both thriving in your own skin and properly managing blood sugars. Undergoing a place of genuine mental health consideration may significantly enhance the overall outcomes and life balance surrounding your diabetes.
Medication and Insulin Management
Diabetes management often requires a multitude of approaches, with medication being the primary one. Recently two main categories of diabetes medicine: insulin and oral hypoglycemic agents are usually required Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps the body regulate its blood sugar levels. In Type 1 diabetes, the body does not produce sufficient insulin itself and therefore needs to receive external injections of it or connect an insulin pump. In Type 2 diabetes, the problem may lie with the body’s inability to properly use insulin- therefore it requires multi-drug therapy.
Oral hypoglycemic agents are also popular alternatives for people who have Type 2 diabetes. Certain types can increase the body’s sensitivity to insulin, some stimulate the production of this hormone from elsewhere, and others cut off metabolizing sugars in the intestines to a great extent. Sulfonylureas, biguanides, and DPP-4 inhibitors are three of the most commonly- prescribed classes of oral medication. Each works differently in the body, so doctors must base their decisions on individual patient circumstances and blood glucose levels. Because diabetics need to keep their blood glucose levels under control, medication compliance must be strictly adhered to.
Missing doses or discontinuing treatment can cause significant fluctuations in blood sugar levels which run then the risk of complication. It is also necessary for patients to frequently check their blood sugar. This will help them get a feel for how their bodies naturally react and it can actually be quite revealing in terms of deciding what medication is appropriate for them. Healthy diabetic lifestyles further require regular meetings with a healthcare professional. Care providers can adjust medicine regimens by following patients closely and responding to their feedback so that diabetic control is optimal. If a patient is experiencing difficulties with their medication, they should feel free to tell their healthcare provider about it. This information can help them make the necessary modifications needed to enhance overall treatment satisfaction. It is important to understand the peculiarities of different drug regimes because of this.
Regular Check-ups and Health Monitoring
Diabetes requires regular check-ups by the sufferer to monitor changes in their health. These tests assist in monitoring the progression of disease, modifying treatment regimens, and reducing complications. These crucial tests are A1C exams, cholesterol tests, and foot checks.
The A1C test is used to gauge how well diabetes is being managed by measuring the average blood glucose levels over several months. While individual targets may vary, an A1C below 7% is often advised for most adults with diabetes. Regular testing enables healthcare providers to recommend improvements in medication and lifestyle changes needed for keeping blood sugar within ideal levels.
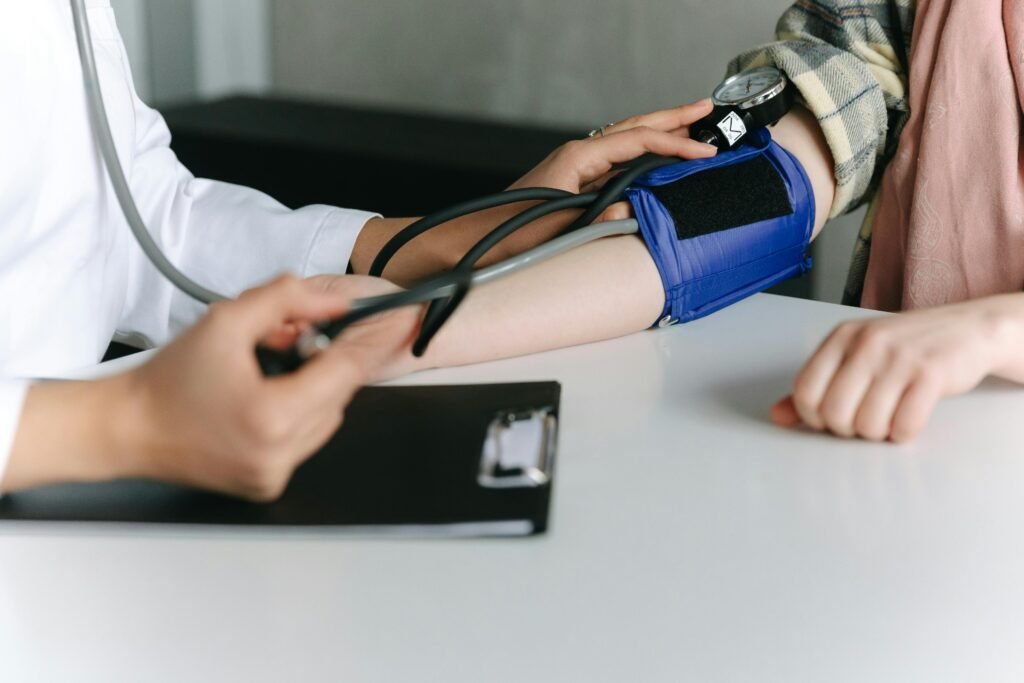
Diabetes monitoring is another important part of the control, and cholesterol checks are also entailed. Because diabetes increases the risk of cardiovascular disease, it is important to screen for and manage lipid profiles. Taking steps to control cholesterol with lifestyle or medications leads to a significantly lower risk of heart disease, a diabetes complication.
Diabetes can cause neuropathy (often in the feet). if a person does not feel their skin is being scraped or punctured, they may have an undetected foot infection that could progress to other complications. Foot exams both by health care professionals as well at home can help six in the early identification of problems, and preventing catastrophic end results.
In addition, working with a multidisciplinary team is vital. These may include endocrinologists, dietitians diabetic educators with primary care physicians. Together they offer patients a combination of experiences that allows them to care for their patients with holistic and personalized views. It is important to proactively manage our health through regular check-ups and screenings so that we are aware of the current state of our body and make informed decisions.
Lifestyle Modifications and Long-term Management
The diabetic lifestyle needs to be sustainable and meant for the long term, it must be a real meaningful life change that will help you manage your condition. One of the most important things that must never be ignored, is balance in our diet and activity. An ancient study includes the use of a wide variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in the diet along with portion control; also keeping an eye on carbohydrate intake. People should learn how to count carbohydrates, which can be a powerful way for people with diabetes type 2 to control their blood sugar well. Finally, physical activity also plays a key role as well; adding both Aerobic exercises and strength training in your lifestyle for at least 150 minutes per week benefits insulin sensitivity of the body along with health.
Another crucial aspect of managing diabetes effectively is by educating oneself more about the condition. Patients should work toward understanding the disease process, its complications, and monitoring requirements. Armed with this new information, they can then make choices that support their goals of health. How to Manipulate Blood Sugar With Food Healthcare teams, such as doctors, dietitians, and diabetes educators offer important resources to keep an eye out for new information and technologies that help us with better management of our diabetes.
For more about lifestyle, you can visit How to Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle

Influences on healthy goals Set realistic healthYou must set a reasonable target that may contribute to long-term positive results. A goal is realistic if it can be objectively achieved, such as losing a defined amount of weight or lowering blood sugar levels; another good type we monitor is exercise. These goals can often be improved greatly by applying the SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable Realistic, and Time-bound)criteria. Additionally, creating a matter with interactions from family and community members can be an advantageous factor as well. Involving them in health-based acts like meal plans and exercises breeds a sense of responsibility, even further facilitating motivation. Support groups are also a way to get extra motivation and emotional support needed to stay positive during your years of diabetes management.
Support Systems and Resources
Dealing with diabetes is really difficult because it’s a lot to deal with and without the right resources we can feel almost powerless. Those who are diagnosed with diabetes should look for a total care program that provides diet and exercise information as well as diabetic self-monitoring techniques. Multiple companies deliver structured programs containing material that enables the patient to self-manage effectively. For example, the American Diabetes Association has workshops on varying parts of diabetes care to provide you a good base for future health.
Along with formal educational programs, peer support groups are vital in assisting the members to effectively cope with their condition from an emotional and psychological perspective. Finding others who have had similar experiences puts us among our “tribe,” and helps to relieve the isolation that we feel, which benefits overall health. Keep in mind there are local and online support groups where you can also share your journey, cheer each other on, and exchange resources — all about supporting one another.
Online resources are an essential tool to help those with diabetes. Access to information — patients can find articles, videos, and forums for tips on up-to-date ways of managing their condition. Sites like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) or Diabetes. com have the information about diabetes and manage it between themselves. This allows users to continuously track blood sugars, nutrition, and physical activity with the use of health apps that can aid in self-management and improved standard of care.

Lastly, ensure that you have a working relationship with healthcare professionals as this is key to the successful management of diabetes. Routine appointments with your doctor, dietitian, and diabetes educator can help you receive personalized guidance that best suits you. An integral part of diabetes management will always be support and advice from both a personal network as well a professional council with regard to holistic living. For more details Diabetic

Hasanpaşa su kaçak tespiti Zeytinburnu’nda su kaçağı tespiti için çok iyi bir ekip. Sorunumuzu hemen çözdüler. https://www.flexsocialbox.com/ustaelektrikci
You actually make it seem really easy along with your presentation but I to find this matter to be actually something which I believe I would never understand. It kind of feels too complicated and very wide for me. I am looking forward for your next submit, I¦ll attempt to get the dangle of it!
Thank you very much for your valuable feedback. You can check more articles too.
me encantei com este site. Pra saber mais detalhes acesse o site e descubra mais. Todas as informações contidas são conteúdos relevantes e exclusivos. Tudo que você precisa saber está ta lá.
Your devotion and passion truly stand out in every paragraph you compose. It’s truly inspiring.