Introduction to Gut Health
Gut health refers to the well-being of the digestive system, encompassing the intricate balance of bacteria, enzymes, and other microorganisms residing in the gastrointestinal tract. This delicate ecosystem, often referred to as the gut microbiome, plays a critical role in various bodily functions, including digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune system support. The gut’s primary responsibility is to break down food, extract essential nutrients, and eliminate waste, but its influence extends far beyond digestion.
One of the essential functions of a healthy gut is its involvement in immune function. Approximately 70% of the body’s immune cells are located in the gut, underscoring its importance in maintaining a strong immune response. A diverse and balanced microbiome can help protect against infections and diseases by supporting the production of beneficial compounds that enhance immune function. Moreover, gut health is also linked to metabolic processes, as it assists in regulating energy balance and fat storage. An imbalance in gut bacteria can lead to metabolic disorders, contributing to obesity and related diseases.

In recent years, there has been a notable increase in interest and research surrounding gut health. Scientific studies have revealed that a healthy gut can influence not just physical health but also mental well-being. The emerging field of psychobiotics explores the connection between gut microbiota and mental health, highlighting how gut health can impact mood and cognitive function. This growing recognition of the gut’s significance has led to an increase in preventive measures, dietary modifications, and probiotic supplements aimed at optimizing gut health. As we continue to unravel the complexities of the gut microbiome, it becomes increasingly clear that prioritizing gut health is essential for achieving better overall wellness.
The Gut Microbiome Explained
The gut microbiome refers to the diverse community of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microbes, residing within the digestive tract. This intricate ecosystem plays a pivotal role in maintaining overall gut health, influencing various physiological functions and systems throughout the body. Each individual’s microbiome is unique and shaped by factors such as diet, lifestyle, and environmental exposures. Collectively, these microorganisms contribute to processes such as digestion, metabolism, and immune system regulation.

Research has illuminated the profound impact of the gut microbiome on mental and physical health. For instance, certain gut bacteria are associated with the production of neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, which can influence mood and emotional well-being. This connection between gut health and mental health has sparked interest in the concept of the “gut-brain axis,” highlighting how changes in the gut microbiome can affect brain function and vice versa. Furthermore, a well-balanced microbiome supports the gut’s barrier functions, preventing the entry of harmful pathogens into the bloodstream, thereby promoting overall health.
Conversely, dysbiosis—a condition characterized by an imbalance in the gut microbiome—can lead to various health issues. Factors contributing to dysbiosis include poor diet, chronic stress, antibiotic use, and lack of physical activity. The implications of dysbiosis are far-reaching, potentially resulting in gastrointestinal disorders, obesity, autoimmune diseases, and even mental health concerns. Therefore, understanding the gut microbiome’s role is essential for recognizing the importance of maintaining a balanced microbial community and the significant effects it has on overall health.
The Connection Between Gut Health and Overall Well-being
Gut health plays a pivotal role in overall well-being, influencing a multitude of bodily functions and systems. The gut is often referred to as the “second brain” due to its intricate relationship with mental health and emotional balance. Research has shown that an imbalance in gut microbiota can contribute to various conditions such as anxiety, depression, and other mood disorders. The gut produces neurotransmitters, including serotonin, which serves as a critical link between gastrointestinal function and emotional regulation.
Moreover, the connection between gut health and autoimmune diseases has garnered increasing interest in recent years. An unhealthy gut can disrupt the intestinal barrier, allowing toxins and pathogens to enter the bloodstream and trigger an immune response. This dysregulation may contribute to the development or exacerbation of autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. Therefore, maintaining a balanced gut microbiome can be pivotal in managing and preventing such diseases.
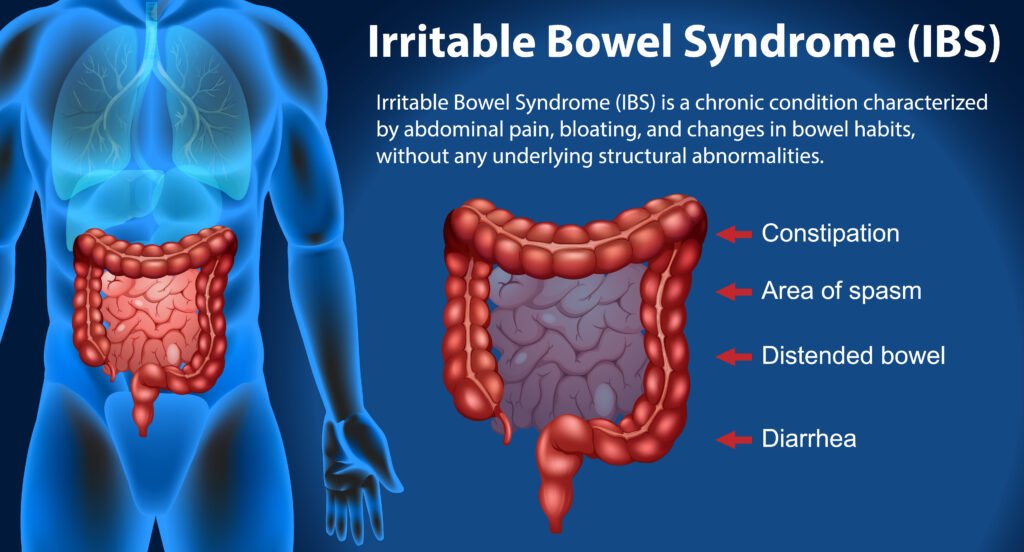
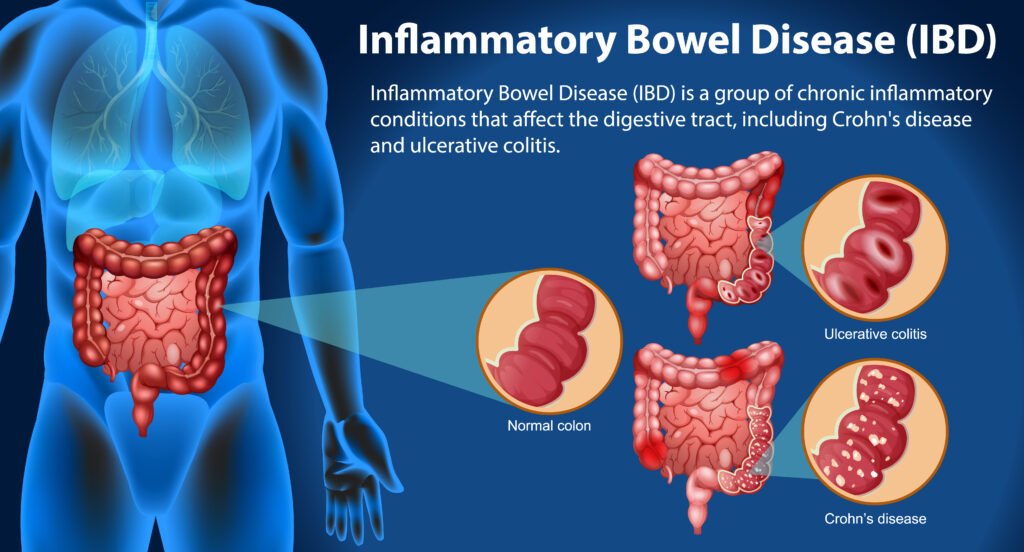
In addition to mental health and autoimmune disorders, gut health also significantly impacts digestive functions. Conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and food intolerances are often linked to imbalances within the gut microbiome. A healthy gut is characterized by a diverse population of beneficial bacteria that aid in digestion, enhance nutrient absorption, and support a robust immune system.
Furthermore, the relationship between gut health and skin conditions like eczema and acne has led to the exploration of gut-skin axis theories. It is believed that an unbalanced gut microbiome may exacerbate skin inflammation and other reactions, indicating the importance of gut health in achieving clear, healthy skin.
In summary, prioritizing gut health is not merely about preventing digestive disorders but is essential for maintaining overall well-being. By fostering a balanced microbiome, individuals may experience enhanced immunity, improved energy levels, and a better mood, underscoring the significance of a healthy gut in holistic health management.
Signs of Poor Gut Health
Maintaining gut health is critical for overall well-being, as a compromised digestive system can manifest through various signs and symptoms. One of the most immediate physical indicators of poor gut health is bloating, which refers to the feeling of fullness or distension in the abdomen. It often arises after consuming certain foods, suggesting that the gut may not effectively process certain substances. Gas, another common symptom, can result from the fermentation of undigested food in the intestines, leading to uncomfortable and sometimes embarrassing situations.

Irregular bowel movements, including constipation and diarrhea, also point to potential gut health issues. Constipation suggests that the digestive system is struggling to process food efficiently, while diarrhea may indicate an overactive gut or an inability to absorb nutrients properly. Both situations can reflect underlying problems with gut bacteria balance and overall digestive function.
In addition to physical manifestations, one’s mental and emotional state can also serve as a significant indicator of gut health. Research has demonstrated a connection between the gut and the brain, often referred to as the gut-brain axis. Consequently, individuals experiencing anxiety or depression may be struggling with gut health issues. Such conditions can be exacerbated by dysbiosis, an imbalance in gut bacteria, leading to altered neurotransmitter levels that influence mood and behavior.
Experiencing fatigue and sleep disturbances is yet another sign of a potential gut health problem. An imbalanced gut can affect the body’s ability to absorb nutrients adequately, leading to deficiencies that contribute to chronic tiredness. Furthermore, studies suggest that gut health can significantly influence sleep quality, making awareness of these signs crucial for overall health. Recognizing these symptoms is an essential first step toward improving gut health and enhancing one’s quality of life.
Dietary Choices for a Healthy Gut
Maintaining a healthy gut is vital for overall well-being, and dietary choices play a crucial role in promoting gut health. One of the fundamental components of a gut-friendly diet is fiber. Fiber-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes help regulate digestion and support the gut microbiome. They encourage the growth of beneficial bacteria, which in turn can enhance digestion and bolster the immune response. Aiming for a daily intake of 25 to 30 grams of fiber can significantly contribute to a thriving gut environment.

In addition to fiber, incorporating probiotics into your diet can be highly beneficial for gut health. Probiotics are live microorganisms, primarily found in fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and miso. These foods introduce beneficial bacteria into the gut, aiding in maintaining a balanced microbiome and potentially reducing the risk of gastrointestinal disorders. Regular consumption of probiotics can also positively impact mental health by promoting the production of neurotransmitters in the gut.

Prebiotics, which are non-digestible fibers that feed and support the growth of good bacteria, are equally important. Foods such as garlic, onions, asparagus, and bananas are excellent sources of prebiotics. They help nourish the gut microbiome, allowing it to flourish and perform its essential functions effectively. Additionally, hydration is paramount in supporting gut health. Water facilitates the digestive process and ensures that nutrients are properly absorbed. A balanced diet, rich in various nutrients, will provide the essential vitamins and minerals that support gut health and overall bodily functions.
By making informed dietary choices, such as increasing fiber intake, incorporating probiotics and prebiotics, prioritizing hydration, and maintaining balanced nutrition, individuals can nurture their gut health and enjoy a better quality of life.
Lifestyle Changes to Support Gut Health
Maintaining optimal gut health transcends dietary choices; lifestyle modifications are crucial in cultivating a balanced microbiome and promoting overall wellness. Among these changes, regular physical activity stands out as essential. Engaging in exercise not only facilitates better digestion by promoting gut motility but also enhances the diversity of gut bacteria. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity weekly, complemented by strength training exercises twice a week. Incorporating simple practices like walking, cycling, or yoga into your day can have significant benefits for gut health.

In addition to physical activity, effectively managing stress is imperative for maintaining a healthy gut. Chronic stress is known to disrupt the gut-brain axis, potentially leading to gastrointestinal issues and impairing the balance of gut microbiota. Techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep-breathing exercises, and progressive muscle relaxation can help mitigate stress levels. Setting aside time for hobbies, social interactions, or simply enjoying nature can foster mental well-being, directly impacting gut health positively.
Adequate sleep is another critical factor that significantly affects gut health. Research has shown a direct correlation between sleep quality and gut microbiome composition. To improve sleep hygiene, aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep by establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and optimizing your sleep environment. Limiting screen time before bed and avoiding caffeine in the late afternoon can further enhance sleep quality.

To summarize, adopting a holistic approach by integrating regular exercise, effective stress management techniques, and prioritizing sleep can significantly bolster your gut health. These lifestyle changes not only support the microbiome but also contribute to better overall health and well-being. Implementing these practices into daily routines can facilitate a balanced and thriving gut environment.
The Role of Supplements in Gut Health
Maintaining optimal gut health is crucial for overall well-being, and supplements can play a significant role in this process. Various types of supplements, notably probiotics, and digestive enzymes, have been recognized for their potential benefits in supporting a healthy gut microbiome. Probiotics are live microorganisms that, when ingested in adequate amounts, provide health benefits by enhancing or restoring gut flora. These beneficial bacteria can help restore balance to the gut microbiome, especially after disruptions caused by antibiotics, poor diet, or illness.
Digestive enzymes, on the other hand, aid in the breakdown of food particles, making nutrients more accessible for absorption. They can be particularly helpful for individuals experiencing digestive issues, such as bloating or discomfort, which may arise from insufficient enzyme production. By supplementing with these enzymes, one could potentially alleviate such symptoms and improve overall digestion.
While supplements can offer support, it is essential to consider them as part of a holistic approach to gut health. Dietary and lifestyle changes, such as incorporating a diverse array of fiber-rich foods, reducing processed sugars, and managing stress levels, should also be pursued. Timing and dosage of supplements matter as well; individuals should consult healthcare professionals to personalize their approach based on specific health needs.
In conclusion, supplements like probiotics and digestive enzymes can be valuable tools for enhancing gut health. By integrating these supplements into a well-rounded plan that includes mindful dietary choices and lifestyle modifications, individuals can foster a healthier gut environment, ultimately contributing to improved digestive function and overall health.
Check out the Superfood
Gut Health and Mental Well-being
Emerging research has increasingly highlighted the intricate relationship between gut health and mental well-being, shedding light on the concept of the gut-brain axis. This axis refers to the bi-directional communication pathway linking the gastrointestinal tract and the brain, a connection that encompasses neural, hormonal, and immunological factors. Studies suggest that the gut microbiome, comprised of trillions of microorganisms residing in the digestive system, plays a pivotal role in influencing mood and mental health.
Several findings indicate that a balanced and diverse gut microbiome can positively impact mental health by modulating the levels of neurotransmitters, including serotonin, dopamine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). These chemicals are vital for regulating emotions and reducing feelings of anxiety and depression. For instance, approximately 90% of serotonin, often dubbed the “feel-good” neurotransmitter, is produced in the gut. Thus, maintaining a healthy gut not only facilitates proper digestion but may also foster emotional stability.
Moreover, gut health impacts mental well-being through its influence on inflammation and stress responses. An imbalance in gut microbiota can lead to increased intestinal permeability, often referred to as “leaky gut,” which allows toxins to enter the bloodstream and provoke systemic inflammation. This inflammatory response has been linked to various mental health issues, including anxiety and depression. Hence, individuals experiencing such conditions may benefit from interventions aimed at improving gut health.
In light of the growing body of evidence linking gut health to mental wellness, adopting a diet rich in prebiotics and probiotics has become a focal point for enhancing mental resilience. Foods like yogurt, kefir, and high-fiber fruits and vegetables support a healthy microbiome, fostering not only physical health but also emotional well-being.
Conclusion and Steps to Take
In conclusion, understanding the importance of gut health is paramount for maintaining overall well-being. As outlined in the previous sections, a balanced gut flora contributes significantly to various body functions, including digestion, immunity, and even mental health. The intricate relationship between gut health and the rest of the body underscores why individuals should prioritize this aspect of their wellness.
To support optimal gut health, there are several actionable steps that individuals can incorporate into their daily routines. First, consider adopting a diet rich in fiber, which can be found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. These foods serve as prebiotics, nourishing the beneficial bacteria residing in the gut. Additionally, including a variety of fermented foods such as yogurt, kimchi, and sauerkraut may enhance the diversity of the gut microbiome, further promoting digestive health.
Hydration also plays a crucial role in gut function. Drinking appropriate water throughout the day can aid digestion and help prevent gastrointestinal issues. Furthermore, individuals should aim to minimize the intake of processed foods and added sugars, as these can negatively impact gut bacteria balance.
Lastly, regular physical activity is vital for encouraging optimal gut health. Exercise has been shown to positively influence gut microbiota composition, enhancing overall metabolic health. Individuals need to find an activity they enjoy to easily incorporate exercise into their routine.
By taking these simple but effective steps, individuals can improve their gut health, positively impacting their overall health. Investing in gut health is an investment in a healthier future, contributing to vitality and wellness for years to come.


I went over this internet site and I think you have a lot of wonderful information, saved to bookmarks (:.
Thank you very much for your valuable feedback. You can check more articles too.